 Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
One of the most important causes of type 1 diabetes is the increase of sugar in the blood. Let us understand how the sugar level increases in the blood. During the process of digestion, most of the food we eat breaks down into sugar (called glucose). Glucose in the bloodstream reaches the body’s cells with the help of a hormone called insulin. And, then our body’s cells use glucose for energy.
Sugar stays in our blood if there is insufficient insulin production. As a result, the sugar level in our body increases leading to a disease called type 1 diabetes. Diabetes is a chronic disease that can damage the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. The diagnosis of type 1 diabetes is more in children, teens, and young adults.
Causes of type 1 diabetes
Causes of type 1 diabetes are not clearly known. But, due to some reason the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Hence, the pancreas doesn’t make insulin, and sugar builds up in the blood leading to type 1 diabetes. Some of the causes of type 1 diabetes are exposure to the illnesses caused by viruses; family history of type 1 diabetes; the presence of antibodies that mistakenly attack own body’s tissues or organs; and, injury to the pancreas by infection, tumor, surgery, or accident.
Risk factors that can cause Type 1 Diabetes
- Not taking the right amount of diabetes medicine at the right time
- Following an incorrect diet plan
- Not doing enough exercise
- Having an illness, like the flu
- Stress
- Smoking
- Lack of sleep
- Taking other kinds of medicines that affect the efficacy of diabetes medicines
Complications of Type 1 Diabetes
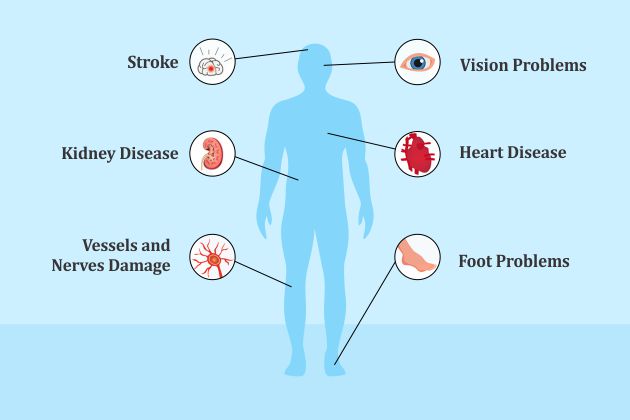
A person with type 1 diabetes may suffer from various health problems such as:
- Vessels and nerves damage
- Increase in the risk of heart disease and stroke, kidney disease
- Vision problems
- Foot problems
- High blood pressure
- Heart attack
- Stroke
How Can Type 1 Diabetes be Managed?
Currently, there is no definite treatment to prevent type 1 diabetes. It can only be managed by:
- Taking insulin properly in the body
- Doing exercise regularly
- Following a healthy diet plan
- Monitoring sugar level and blood pressure regularly at home
If you have symptoms or risk factors of type 1 diabetes, go for an insulin blood test. This test is also called as insulin – fasting test. It is done to measure the amount of insulin present in the blood.