The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front part of your neck that affects most organs in your body. It secretes two hormones, namely triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which enhance nearly all the functions of your body, including metabolism, body weight, and temperature.
What Are The Problems Associated With The Thyroid Gland?
Abnormal levels of T3 and T4 hormones might cause thyroid-related disorders.
Hypothyroidism
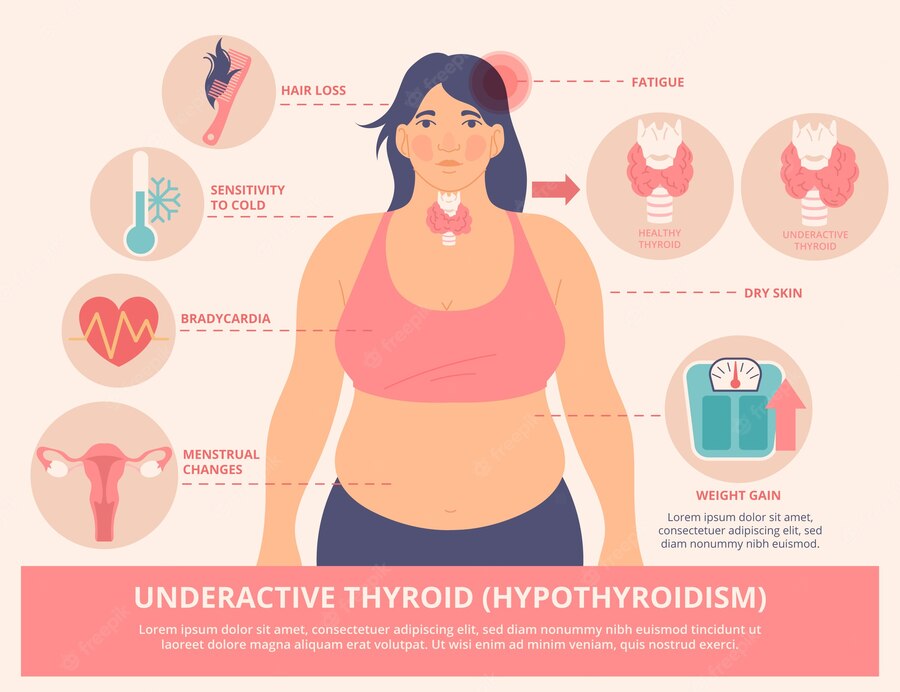
It is a metabolic condition where your thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Its symptoms include weight gain, fatigue, dry skin, constipation, hair loss, etc.
Hyperthyroidism
It is a metabolic disorder which involves excess secretion of thyroid hormones. Its symptoms include irregular heartbeats, weight loss, anxiety, weakness, increased hunger, increased sweating, etc.


Important Tests for Thyroid Health
Thyroid function tests are done by withdrawing blood from a vein in your arm. These blood tests help check if your thyroid is functioning properly. Also, the tests help monitor treatment in people with already existing thyroid problems.
-
T3 and T4 Test:
The thyroid gland primarily produces T4 along with T3 in smaller amounts. T3 and T4 tests help evaluate thyroid functions. These tests measure the level of T3 and T4 hormones in the blood. High levels of these hormones indicate hyperthyroidism whereas low levels indicate hypothyroidism.
-
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test:
The pituitary gland secretes TSH. Testing TSH is the most significant way of monitoring how well your thyroid gland is functioning. If the thyroid gland is secreting too much thyroid hormone, the pituitary gland releases less TSH and vice versa. Hence, TSH along with T3 and T4 tests aid in the detection of thyroid problems effectively.
-
FT3 and FT4 Test:
FT3 and FT4 are the free forms of the thyroid hormones. High levels of free thyroid hormones in the blood may indicate an overactive thyroid, whereas low levels may indicate an underactive thyroid.
-
Antimicrosomal and Antithyroglobulin Antibody Test:
Some patients develop autoimmune diseases, in which their immune system attacks their own cells and organs. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis is one such disorder that affects the thyroid and increases levels of specific antibodies. Antimicrosomal and antithyroglobulin antibody tests help detect such antibodies.
-
Neonatal TSH:
Neonatal TSH is useful for detecting thyroid diseases in infants.
-
Ultra Sensitive TSH:
This is the rapid way of detecting thyroid disorders. An ultra-sensitive TSH test allows early detection of any rise in TSH levels.
Benefits of Regular Thyroid Testing
Don’t forget to keep a regular track of your thyroid function with the help of thyroid tests.
- Thyroid testing evaluates the level of thyroid hormones. Thus, effectively help diagnose thyroid-related disorders.
- It checks the effectiveness of treatment or management plans for thyroid disorders.
Regular thyroid testing not only helps in the diagnosis of thyroid disorders but also helps determine other related conditions such as high cholesterol, hypertension and diabetes.






